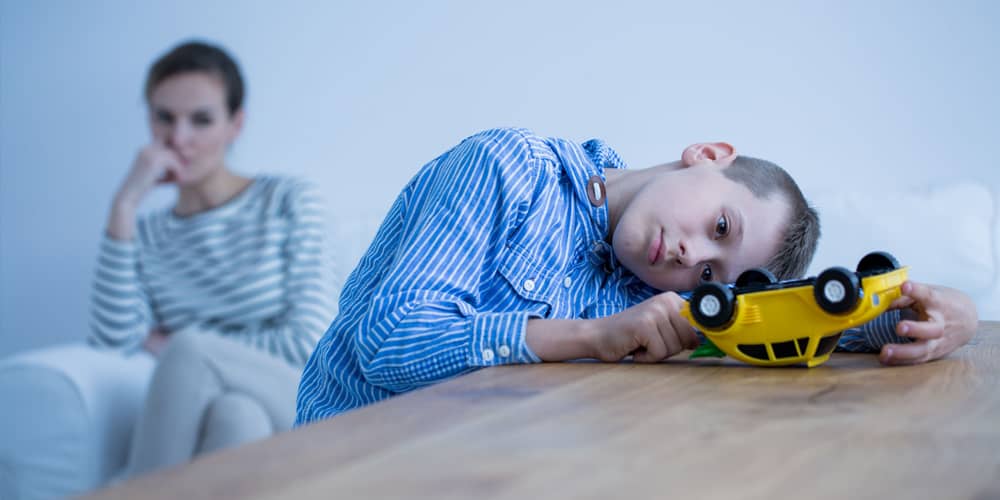
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects individuals in various ways. One of the key aspects of autism that significantly impacts daily life is sensory processing. For individuals with autism, the world can be a sensory minefield, where everyday experiences can become overwhelming due to heightened sensitivities or, conversely, diminished responses to sensory stimuli.
Understanding Sensory Processing in Autism
Sensory processing refers to the way the nervous system receives, organizes, and interprets information from the environment. For individuals with autism, this process can be atypical, leading to challenges in managing sensory input. Imagine a world where ordinary sounds are amplified, lights are blinding, and textures evoke intense discomfort – this is the reality for many on the autism spectrum.
Hyper- and Hypo-Sensitivities: Striking the Balance
Individuals with autism often experience either hyper-sensitivities or hypo-sensitivities, sometimes both, across various senses. Hyper-sensitivities can manifest as acute responses to stimuli, such as being distressed by loud noises or unable to tolerate certain textures. On the other hand, hypo-sensitivities may lead to a reduced awareness of stimuli, requiring more intense input to register sensations.
Creating an Autism-Friendly Environment
Understanding sensory processing challenges is crucial for creating environments that support individuals with autism. Simple adjustments, such as using soft lighting, providing noise-canceling headphones, or offering sensory-friendly spaces, can make a significant difference. Whether at home, school, or in public spaces, fostering awareness and making accommodations helps unravel the sensory puzzle for those with autism.
The Impact on Daily Life
Sensory processing difficulties can influence various aspects of daily life, from personal care routines to social interactions. For some individuals, routines and rituals serve as coping mechanisms to manage sensory input. Others may develop specific interests or engage in repetitive behaviors to self-regulate and navigate their sensory environment.
Therapeutic Approaches to Sensory Processing
Occupational therapy tailored to sensory integration is often a cornerstone in supporting individuals with autism. Therapists work collaboratively with individuals to address sensory challenges, gradually helping them adapt to and manage different stimuli. Techniques may include sensory diets, exposure therapy, and the use of sensory tools to promote self-regulation.
The Individuality of Sensory Experiences in Autism
It’s essential to recognize that sensory experiences vary widely among individuals with autism. What may be soothing for one person might be distressing for another. Acknowledging and respecting these individual differences is crucial for creating inclusive and supportive environments.
Conclusion
Autism and sensory processing are interconnected elements that shape the way individuals experience and interact with the world. By unraveling the sensory puzzle, we can enhance our understanding of the unique challenges faced by those with autism and work towards creating a more inclusive society. Through awareness, education, and empathy, we can pave the way for a world that embraces and accommodates the diverse sensory experiences of individuals on the autism spectrum.